

Important information for your patients
when purchasing an Omega 3
fish oil
The benefits of taking Omega3 fish oil are well
documented. There are 2 main beneficial components to fish oil that you need to
know about (
eicosapentaenoic
acid
(EPA), and docosahexaenoic
acid
(DHA). When
purchasing Omega 3 Fish Oil you should be looking for the highest amount of
milligrams (mg) of EPA and
DHA
Omega-3’s EPA (Eicosapentanoic Acid) and DHA
(Docosahexanoic Acid) are the main components of the brain’s neurons and all
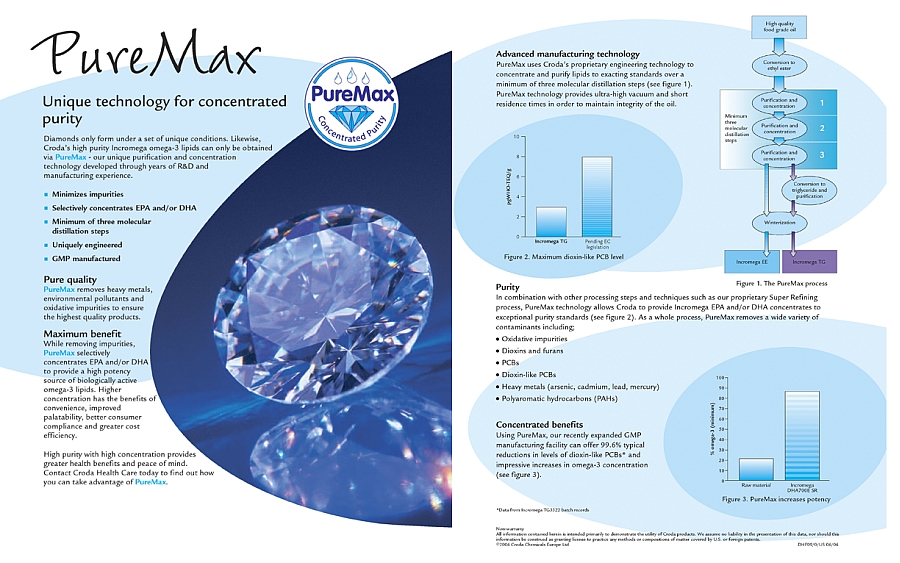
cell membranes. Chiropractor's Blend Ultra Pure Omega3 utilizes the PureMax® system,
which uses a proprietary engineering technology to concentrate and purify
lipids to exacting standards over a minimum of three molecular distillation
steps. PureMax® offers a 99.6% typical reductions in levels of dioxin-like PCBs
and impressive increases in omega-3 concentration.
THE
AMOUNT OF EPA
AND DHA PER SERVING MUST BE
SUFFICIENT
COMPARE CHIROPRACTOR’S BLEND OMEGA3 TO OTHER OMEGA3 PRODUCTS
Your patients should be looking
for the highest Milligrams (MG) of EPA and
DHA.
Compare ours to all others selling
Omega3 fish oil. Check the amount of EPA and
DHA in their
product. Chiropractor’s Blend Omega3 fish oil offers 2,800mg's of Fish Oil, 860mg’s of EPA
eicosapentaenoic
acid
and 580mg of DHA docosahexaenoic
acid.
PLUS OUR OMEGA3’S ARE ENTERIC COATED, NO FISHY AFTERTASTE OR BURPING
All about Chiropractor's Blend Fish Oil

Ultra Pure Omega3 1440™ is cutting edge Essential Fatty
Acids (EFAs). Because our bodies do not manufacture EFAs on their own, Ultra
Pure Omega3 1440™ provides these "necessary for life" fatty acids
that have been shown to be deficient in the "standard American diet."
EFAs have been shown to
have a profound effect on the production of
prostaglandins. EFAs support healthy blood circulation, normal blood pressure,
may reduce inflammation and help balance bodily fluids. EFAs promote optimal
cardiovascular, skin, nervous system and immune health. They are necessary for
maintai
ning bone health, regulating your metabolism and to maintain
reproductive capabilities. Omega-3’s EPA (Eicosapentanoic Acid) and
DHA
(Docosahexanoic Acid) are the main components of the brain’s neurons and all
cell membranes.
Ultra Pure Omega3
1440™ utilizes the PureMax® system, which uses a proprietary engineering
technology to concentrate and purify lipids to exacting standards over a
minimum of three molecular distillation steps. PureMax® offers a 99.6% typical
reductions in levels of dioxin-like PCBs and impressive increases in omega-3
concentration.
PureMax® is a trade mark of croda international plc england
Here’s just one clinical trial
from hundreds of studies you should read:
A
clinical trial has been published from
Italy which has evaluated the effect of omega-3 supplementation
on cognitive performance in normal healthy adults with mean ages of 33 years.
This study indicated that supplementation with
800 mg of DHA plus 1600 mg of EPA for a 35 day period was
associated with an improvement in the profile of mood state as measured by the
POMS (Profile of Mood Stage) analysis. The POMS analysis showed an increase of
vigor and a decrease of the other mood states (anger, anxiety, fatigue,
depression, confusion).
Sixty per cent of the human brain
consists of fat, polyunsaturated fatty acids such as
DHA in
particular.
DHA is essential to brain functions, but it is also essential
for the prevention of brain cell damage. Poor memory, and particularly dementia
such as Alzheimer s disease, is associated with low concentrations of brain
DHA.
People with a regular intake of seafood have a lower risk of developing
dementia.

Good Fats and Bad Fats
There are good fats and bad fats. Bad fats
include trans fatty acids, which are artificially produced, and saturated fats,
which come from animal products. While the bad fats should be kept to a minimum
in everyone’s diet, good fats should also be consumed in moderation.
Calorie-wise they both are equivalent; however, how they are used and how they
react in our bodies is quite different.
Essential Fatty Acids
(EFA)
Essential Fatty Acids (EFA) – Omega-3 and
its importance to our bodies. Our bodies do not manufacture EFAs on their own;
therefore, it is necessary to get them from our diet, by direct intake from
food or supplement sources, on a daily basis. The name alone gives away the
fact that this particular fatty acid is "essential" to our life as it
is required for our health and protection from illness. EFAs are needed for the
proper function of every cell, tissue, organ and gland in the body. Numerous
scientific studies have shown the necessity for omega-3s and the dangers of our
standard American diet being so severely deficient in them while it is
excessively sufficient in omega-6s, mainly from processed foods.
Omega-3 eicosapentanoic
acid (EPA) and docosahexanoic acid (
DHA)
Omega-3 fatty acids, a class of essential
polyunsaturated fatty acids, are most deficient in the Western diet. Foods high
in omega-3 eicosapentanoic acid (EPA) and docosahexanoic acid (
DHA) include salmon,
halibut, mackerel, sardines, albacore, lake trout and herring. According to Dr.
Allan Spreen, a nutrition expert and Director of "The Nutrition
Physician," EPA and
DHA are the two Omega-3s
that have the best effects on human biochemistry, and they are contained in
higher amounts in fish oil. Omega-3 alpha-linolenic acid (
ALA) is found in some nuts
(such as English walnuts) and their oils, leafy green vegetables such as
spinach, tofu and other forms of soybeans, and vegetable oils such as canola,
soybean, flaxseed/linseed and olive. The body converts
ALA to EPA and DHA; however, as we age,
the conversion process can become insufficient for what our bodies need.
Research has shown that the standard
American diet being so dangerously deficient in the very essential omega-3
fatty acids and so dangerously toxic in the essential omega-6 fatty acids are
common factors in the alarming numbers of preventable illnesses and
disease-related deaths in the U.S. Deficiencies in EPA and
DHA omega-3 fish oil are
being linked to severe illnesses and disorders that begin in childhood and
continue throughout our life spans. EPA and
DHA are so important
because they are the main component of the brain neurons and all cell
membranes. For children, due to the lack of EFAs, some of what is appearing at
early ages is asthma and developmental, learning and behavioral problems such
as Attention Deficit Disorder/Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Teens
and adults are developing diabetes, obesity, depression, skin and digestive
disorders, hormonal problems, high blood pressure and high cholesterol, vision
problems, infertility, pregnancy complications such as poor fetal development,
premature birth and postpartum depression, chronic pain, an inability to fight
infection and/or heal wounds, heart disease, strokes, and breast, colon and
prostate cancers. Our elderly population has seen an increase in arthritis,
osteoporosis, mood disorders and Alzheimer’s. While there can be other
contributing causes for these disorders and illnesses, a lack of proper
nutrition, including the consistent deficiency in omega-3s, is leading to many
of these preventable diseases, disorders and earlier deaths than necessary.
As a result, scientific studies are
repeatedly proving the necessity for supplementing our diets with EPA and
DHA omega-3 fish oil. The
American Heart Association (AHA) released its science advisory "Fish
Consumption, Fish Oil, Lipids and Coronary Heart Disease" in 1996. Since
then, the evidence has continued to mount that shows EFAs can reduce the risk
of sudden cardiac death, may improve one’s blood lipid cholesterol and lower
triglycerides levels, while decreasing the risk of coronary heart disease. The
AHA showed newer findings again in November 2002 when they released their
scientific statement "Fish Consumption, Fish Oil, Omega-3 Fatty Acids and
Cardiovascular Disease."
Since then, the evidence in multiple
studies still continues to mount. EFAs have been shown to have a profound
effect on the production of prostaglandins (hormone-like substances that render
many positive effects in your body) and they support healthy blood circulation,
normal blood pressure, may reduce inflammation and help balance bodily fluids.
EFAs promote optimal cardiovascular, skin, nervous system and immune health.
They are necessary for maintaining bone health, regulating your metabolism and
to maintain reproductive capabilities. The human brain is more than 60%
structural fat, of which
DHA is the major
polyunsaturated fatty acid found in the brain. This important EFA is needed for
brain development, function and to compose the neural synapses. Low levels in
our brains are associated with the increased tendency toward depression,
suicide and violence, as well as memory loss, impaired cognitive function and
Alzheimer’s. Studies have shown omega-3 helps improve cell function in the lining
of the heart and blood vessels, lowers triglyceride levels, and inhibits
platelet clumping.
While research is continuing and the
evidence is building as to our need for omega-3s, I would like to list just a
little of what has already been found without going into all the details of the
studies.
• The University of Colorado at Denver conducted a study using
1,770 children (beginning age of birth to 3 years old and continuing for an
average of 6 years) who were at high risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Increasing Omega-3 intake was associated with a 55 percent reduction in their
risk. Lead researcher Jill M. Norris,
MPH, PhD, said, "Our
study suggests that higher consumption of total Omega-3 fatty acids, which was
reported on the FFQ, is associated with a lower risk of islet autoimmunity in
children at increased genetic risk of type 1 diabetes." This study appeared
in the
September 27, 2007 (vol. 298; pp
1420-1428) issue of "The Journal of the American Medical
Association."
• A study published in "Rheumatology
2008; March 24" was done by the Ninewells Hospital and Medical School in
Dundee, the Western General Hospital in Edinburgh, and the University of
Dundee, all in Scotland, using cod liver oil capsules to treat patients with
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). The study found that using 10 grams of cod liver oil
per day dramatically reduced the need for non-steroidal anti-inflammatories by
30 percent. Ninety-seven people, aged 37 to 78 years old with an average of 13
years of having RA, were enrolled in the study.
• According to a Harvard Study, men with
the highest level of Omega-3 (from fish) in their blood were more than 80% less
likely to die suddenly from heart disease compared to men with the lowest
levels. Harvard also completed a 16-year study on 85,000 women. That study
determined women with the highest intake of Omega-3 (from fish) received
significant support for heart health.
• Many people are looking for an
alternative to Coumadin, a commonly used blood thinner. It thins the blood by
poisoning and killing off the vitamin K in your body. Over time, this will lead
to many other medical problems, some of which are osteoporosis, arterial
calcification and cognitive malfunction. However, a natural alternative is
Omega-3s. Cod liver oil and other fish oils work by making platelets in your
blood so slippery that they can’t stick together to form a clot. In order to
get the proper dose for your body, it is best to work with a healthcare
specialist who is skilled in nutritional/natural medicine. However, this
particular use does not actually having clinical studies to back it up.
In the past, it was possible to get
sufficient amounts of EPA and
DHA by eating wild game
meat and wild fish. Today, the majority of our meat comes from grain fed
domesticated animals, which are deficient in EFAs. Fish is a good source of
protein and it does not contain high saturated fat. However, many fish in our
oceans have become laden with mercury, dioxins and other pollutants. As a
result, we turned to farmed fish which do not have sufficient levels of EFAs
and many are also showing up laden with pollutants. While a recent study (using
data spanning 15 years) from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) suggested
that increased intake of omega-3 oils during pregnancy and lactation led to
higher IQ scores, better hand-eye coordination and more positive social
interaction in children, due to the toxicity of fish, pregnant women are being
told by the NIH to limit or avoid certain fish during pregnancy and while
nursing. Also, as a nation, we consume an insufficient amount of fish to get an
adequate supply of EFAs in our diets, and our children typically do not consume
the fish that are high in EFAs.
A primary source then for an adequate
amount of EPA and
DHA in our diets is through
supplementation with high quality, toxin free fish oil to ensure our health,
vitality and quality of life. Supplementing your diet with omega-3s will not
only help you lead a healthier lifestyle with more vitality physically and
mentally, but it may also help you to avoid developing preventable illnesses
and early death. Omega-3s can oxidize and form free radicals in your body. To
offset this risk, nutrition experts are now advising that we take a daily
vitamin E supplement (as mixed tocopherols).
When consuming fish oil supplements,
caution should be observed by anyone with an allergy or sensitivity to fish. In
this case, fish and/or fish oils are not for everyone. Caution is also needed
by anyone with an allergy or sensitivity to nuts. Alpha linolenic acid or some
omega-3 products may be derived from the types of nuts that cause allergic
reactions. If you experience any gastric (stomach) distress or side effects
such as burping a fishy taste, the effects may be minimized by starting fish
oil supplements with low doses and gradually increasing the dose to the
sufficient amount, and/or taking fish oil supplements with meals. If you are on
blood thinning medication (including aspirin), have a bleeding disorder, take a
very large dose of fish oils, or eat a number of omega-3 fish meals on a weekly
basis, you should be monitored by a qualified health professional as omega-3s
may thin your blood.
To reach or maintain optimum health, there
is a need for a well-rounded diet and supplementation program. If you need
help, and most of us do, in identifying the needs within your nutritional
program for you and your family, talk to your doctor of chiropractic or a
qualified health care specialist.
References: American
Heart Association, Health Science Institute, Healthier News, Henschell
Chiropractic, Iceland Health, Innate Choice, International Health News, Medical
News Today, Medicine Net, Medline Plus, National Institutes of Health, National
Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements, NetWellness Consumer Health
Information, University of Maryland Medical Center, WordNet
Essential Fatty Acids
(EFAs)
All EFAs are fatty acids that cannot be
constructed within the human body by any normal chemical process and therefore
must be obtained from the diet. The term "essential" refers to those
fats directly involved in biological processes, as opposed to those which
simply act as calories (fuel).
In
addition to the 2 Omega-3's,
DHA and EPA, there are
other fatty acids that are critical to health as well.
The first one, and one of the most
interesting, is a type of Omega-6 Linoleic Acid, specifically, Conjugated
Linoleic Acid (CLA), which is found naturally in the meat and dairy products
primarily of ruminants (mammals with 2-stage digestion such as cattle and
bison).
One of the things which makes
CLA so intriguing is that it is a variety of trans fatty acid, a type of
polyunsaturated fat which has gotten a deservedly bad name recently in the
health news.
However, the "bad
news" on trans-fats comes from the chemically-produced, non-natural fat
compounds created by artificially hydrogenating regular vegetable oils.
Hydrogenated, or partially hydrogenated
vegetable oils, create a type of trans-fat which current studies indicate can
do an enormous amount of cardiovascular damage and lead to all types of disease
in general, including heart attack, stroke and cancer.
These types of fat can only be found in
highly processed consumer foods, and do not occur in nature, and they should be
avoided at all costs.
CLA, however, is a type of trans fatty
acid that does occur naturally in meat and dairy products, and studies show
that not only does it not have negative cardiovascular effects that its
chemically created cousins do, in has in fact been shown to do a great deal of
good for the human body.
Antioxidant and
anti-cancer properties have been attributed to CLA, as well as its tendency to
reduce body fat, improve cholesterol levels and decrease glucose uptake.
In terms of human body weight, CLA has been
shown to increase metabolic rates and subsequently decrease body fat,
specifically in the abdominal area, while increasing muscle growth.
As an antioxidant, it appears to increase
glutathione levels in a highly positive manner.
Glutathione is one of the body's key defenses against cellular toxins
such as free radicals, and acts as a cellular defense against cancer.
Since glutathione is manufactured internally,
and external supplementation has not shown to have any significant positive
effects, the best way to get higher glutathione levels is to have a diet rich
in glutathione precursors, which are the essential components that the body
uses to create glutathione itself.
As for CLA's anti-cancer properties,
these appear to be attributed to the recently developed theory that links some
types of cancer to chronic inflammation, something that CLA reduces. Chronic
tissue damage and chronic inflammation leads to an imbalance of pro and
anti-inflammatory cytokines, which some studies indicate may increase the risk
of cancer.
CLA appears to act as an
anti-inflammatory agent as well as a cellular protector in it's capacity as a
glutathione precursor, so, overall, while more conclusive research is required
to both clarify the mechanisms and verify the results, early indications are
clear:
CLA is your body's friend in
health!
Next on our list of "friendly
fats" is Gamma Linoleic Acid, or GLA.
A vegetable relative to CLA's animal based Linoleic Acid, GLA is a polyunsaturated
essential fatty acid derived from several types of plant and plant seeds.
The evening primrose plant was grown by
Native Americans to treat swelling in the body, and in the 17th century, it was
exported to
Europe where it became a
popular folk remedy named king's cure-all.
It was from the seeds of this plant that GLA was first isolated in
1919.
Research continues on GLA's
anti-inflammatory properties, since it shows great promise and has none of the
side-effects of other pharmaceutical anti-inflammatory medicines.
Herbal medicine advocates recommend GLA
especially in assisting with auto-immune disorders, arthritis, and eczema.
It's anti-inflammatory properties may be the
source of the early studies which suggest that GLA has unique properties with
potential to suppress tumor growth and retard or prevent metastasis.
GLA is one of the body's first
biochemical step in the transforming linoleic acid into important and
beneficial prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are essential to the proper
functioning of each cell, while essential fatty acids formed from GLA are
required for each cell's structure.
While evening primrose oil is a good source of GLA, nature's most potent
concentration of GLA comes in the form of borage seed oil (24%).
Scientists continue to discover the
regulating effects of prostaglandins, but it seems clear that without the
essential fatty acids, the building blocks of prostaglandins, the body's fat
metabolism is certain to malfunction.
So
make certain you are getting adequate levels of GLA in your diet, through
supplementation or consumption of borage or other GLA-containing seed oils.
Last, but not least, on our list of
fats that are essential to bodily health, is "the other half" of the
Linoleic Acid puzzle, if you will…Alpha Linoleic Acid, or,
ALA.This one is an Omega-3 polyunsaturated
essential fatty acid, and since it has a distinct molecular pattern different
from the Omega-6 GLA,
ALA provides the other half
of that nutrient set.
Studies have found
evidence that
ALA is related to a lower
risk of cardiovascular disease, however, the mechanism is still unclear.
We know that the body converts ALA into the longer chain
fatty acids EPA and
DHA which we discussed in
our previous article, but it is unknown whether the protective effect against
cardiac arrhythmia is exerted by
ALA itself, or by these
metabolic products. Research has also suggested a major neuroprotective effect
of
ALA in in-vivo models of
both global ischemia and KA-induced epilepsy.
ALA can be found in a
variety of plants (including the chia, kiwi, lingonberry and hemp), but it is
most commonly available in flaxseed oil (55%).
Intriguingly, because ALA is present at just 8%
in the worlds most common edible oil, soybean oil, and because
ALA is a highly unsaturated
fat which is therefore very liquid at room temperature, it is
ALA which essentially
caused much of the current trend toward trans-fats.
Current Soybean oils must be partially
hydrogenated in order to be stable at room temperature.
Now, remember, ALA itself is not a
trans-fat, nor is it chemically created, it is entirely natural…it isn't
ALA's fault that it is
liquid at room temperature!
Interestingly, DuPont is actually trying to engineer a ultra-low ALA soybean, so that they
would no longer have to hydrogenate the oil to get the desired effect.
In any event, soybean oil has never been a
sufficient provider of
ALA in the diet to begin
with.
Dietary ALA has been assessed for
its role in cardiovascular health and clinical benefits have been seen in some
but not all studies. Still, a review in 2005 concluded "The weight of the
evidence favors recommendations for modest dietary consumption of
ALA for the primary and
secondary prevention of
CHD."
To review, DHA and EPA are a pair of
multi-beneficial Omega-3 fatty acids primarily found in fish oils.
CLA is a "good", naturally
occurring trans fatty acid found in some types of animals, most notably cattle
and other range-dwelling herbivores.
GLA
is a vegetable-based Omega-6 fatty acid with many beneficial properties
including that of a natural anti-inflammatory agent, and it is best found in
borage seed oil.
Lastly, ALA is a vegetable-based
Omega-3 fatty acid found most available in flaxseed oil, and it converts inside
the body into
DHA and EPA as well.Each of these EFAs plays a crucial role in
regulating your bodies internal functions, from cellular stability to
neurotransmission, from toxin defense to inflammation control, from beneficial
cholesterol levels to proper glucose absorption.
Without a doubt, we cannot live without
EFAs…but without the proper diet or supplementation, we tend to get far too few
of them.
So bulk up on your EFA-containing
foods, and supplement your EFAs in order to bring your body into total wellness.
Sources: Cancer and
Inflammation (CIBA Foundation Symposia Series) 2004 by Jamie A. Goode, Bellury
M.A. Dietary Conjugated Linoleic Acid in Health: Physiological Effects and
Mechanisms of Action Ann Rev Nutr 22:505-31, 2002, Belury, M.A.. Inhibition of
Carcinogenesis by Conjugated Linoleic Acid Potential Mechanisms of Action. J.
Nutr 132:2995-98, 2002,
French, P. et
al. J Anim Sci Nov;78:2849-55, 2000, Mozaffarian D (2005). "Does
_-linolenic acid intake reduce the risk of coronary heart disease? A review of
the evidence". Alternative therapies in health and medicine 11 (3): 24–30;
quiz 31, 79, William E. Connor (2000). "Importance of n_3 fatty acids in
health and disease" (pdf). American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 71 (1
Suppl.): 171S–175S,
Blankson H,
Stakkestad JA, Fagertun H, Thom E, Wadstein J, Gudmundsen O. (December 2000).
"Conjugated linoleic acid reduces body fat mass in overweight and obese
humans". Journal of Nutrition 130 (12): 2943–2948,
"Plant oil 'acts like cancer drug'"
(2005-11-02). (describing work by Dr Javier Menendez and colleagues at
Northwestern University and published in Journal of the National Cancer
Institute), Fan, Yang-Yi and Robert S. Chapkin (9 September 1998).
"Importance of Dietary Omega-Linolenic Acid in Human Health and
Nutrition". Journal of Nutrition 128 (9): 1411–1414, Yung-Sheng Huang,
Vincent A. Ziboh (2001). Gamma-Linolenic Acid: Recent Advances in Biotechnology
and Clinical Applications. AOCS Press, 259. ISBN 1893997170.
Warning:
Pregnant or lactating women, diabetics, hypoglycemics and people with known
medical conditions and/or taking drugs should consult with a licensed physician
and/or pharmacist prior to taking dietary supplements. This statement has not
been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
This product is not intended to diagnose,
treat, cure or prevent any disease.